Providing science-based guidance on microbial issues for more efficient food safety systems
Objectives
The Task Force aims at facilitating the development of harmonised, science-based approaches to predict and prevent risks. Those approaches may serve as decision making support for regulators and food industry.
Reviewing the existing knowledge on current and (re-) emerging pathogen behaviour and ecology is also key. The Task Force will also try to answer the reason why the pathogens persist by detecting and typing methods, as well as reviewing potential control options available.
Impact
This Task Force has published 9 peer reviewed publications and 4 Black & White reports in less than 9 years. Its significant
contribution to the state-of-the-art and its research findings are widely spread. The Task Force frequently collaborates with the International Association for Food Protection International (IAFP).
Since 2016 they have organised 12 dissemination activities such as the round tables and follow-up webinar, webinars
and sessions at the IAFP Annual Meeting and IAFP European symposium.
For more detailed information, please contact Angeliki Stavropoulou at astavropoulou@ilsieurope.be or Toula Aslanidis at taslanidis@ilsieurope.be
Task Force Members
| Dr Anett Winkler – Chair | Cargill | Food Safety Advisor | DE |
| Dr Christophe Dufour – Vice-Chair | Institut Mérieux (bioMérieux Industry) | Scientific Director Microbiology | FR |
| Prof. Marcel Zwietering – Co-Chair | University of Wageningen | Professor | NL |
| Dr Roy Betts* | Campden BRI | Head of Microbiology | UK |
| Dr Polly Courtney | General Mills | Food Safety Technical Team Manager | US |
| Dr Intisar Khan | Mondelēz International | Global Food Safety Programs Director | UK |
| Dr Angeliki Stavropoulou | ILSI Europe | Scientific Project Manager | BE |
*Scientific Advisor
Expert Groups
Environmental Monitoring in Dry production environments – Are we looking for the right thing(s) / microorganism?
Background & Objectives
Environmental monitoring (EM) program are gaining increasing importance in the context of food safety plans / HACCP programs.
Recent outbreaks have shown the relevance of the environment to ensure the safety of products. However, there are still many uncertainties on how to set up a meaningful program, which would provide early warnings of potential product contamination.
Output
- The current activity aims to evaluate existing scientific information on microorganisms of importance and/or concern in dry production environments.
- The resulting evaluation would help industry and regulators to focus and set up targeted EM programs depending on their purpose.
Process Validation Study Protocols for Control Measures of Foodborne Pathogens in Foods – Completed
Background & Objectives
There are no generic protocols available to guide manufacturers and ensure that all relevant aspects are considered when undertaking a validation. The expert group aims to develop a recommended protocol to control foodborne pathogens in various food matrices.
Output
This publication will help to establish an industry wide standard protocol to validate the critical control points (CCP) in the Hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) plan. It will also eliminate or reduce the variation issues among food safety professionals, consultants and third party laboratories to conduct a validation study.
The output would especially support small and medium size businesses that have fewer resources to those tasks available. It would also improve the overall understanding of validation processes in practice.
Expert Group Members
Environmental Monitoring in Dry production environments – Are we looking for the right thing(s) / microorganism?
| Dr Francois Bourdichon – Chair | Catholic University of Sacred Heart | Researcher | IT |
| Dr Anett Winkler – Vice-Chair | Cargill | Food Safety Advisor | DE |
| Dr Roy Betts | Campden BRI | Head of Microbiology | UK |
| Dr Christophe Dufour | Institut Mérieux (Mérieux NutriSciences) | Scientific Director Microbiology | FR |
| Prof. Seamus Fanning | University College Dublin | Professor | IE |
| Prof. Jeff Farber | Food Safety & Quality Assurance Program | Professor | CA |
| Dr Ellen Wemmenhove | Arla Foods | Senior Scientist | DK |
| Prof. Marcel Zwietering | University of Wageningen | Professor | NL |
| Dr Angeliki Stavropoulou | ILSI Europe | Scientific Project Manager | BE |
Process Validation Study Protocols for Control Measures of Foodborne Pathogens in Foods – Completed
Dr Heidy den Besten – Chair University of Wageningen Assistant Professor NL Dr Erdogan Ceylan – Vice-Chair Institut Mérieux Director of Research US Dr Alejandro Amezquita Unilever R&D Programme Director UK Dr Nathan Anderson US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Agricultural Engineer US Dr Roy Betts Campden BRI Head of Microbiology UK Dr Laurence Blayo Nestlé Research Center Group Leader Food Safety and Microbiology CH Dr Francisco Garcés-Vega Consultant Consultant CO Dr Elissavet Gkogka Arla Foods Research Microbiologist DK Prof. Linda Harris University of California Professor US Dr Peter McClure Mondelēz International Microbiology Section Manager UK Dr Anett Winkler Cargill Food Safety Advisor DE Dr Angeliki Stavropoulou ILSI Europe Scientific Project Manager BE
Publications
The task force organised a webinar designed for industry experts and regulatory agencies on the relevance of end-product testing in food safety management, on November 2015, with the support of IAFP.’
All Publications
Processing Environment Monitoring in Low Moisture Food Production Facilities. Are we looking for the right microorganisms?
International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2021
109351, ISSN 0168-1605, Commissioned by the Microbiological Food Safety Task Force.
Guidance on validation of lethal control measures for foodborne pathogens in foods
2021
Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2021;20,3:2825-2881. Commissioned by the Microbiological Food Safety Task Force.
The Use of Next Generation Sequencing for Improving Food Safety: Translation into Practice
2019
Food Microbiology 2019;79:96-115. Commissioned by the Microbiological Food Safety Task Force.
Foodborne Viruses: Detection, Risk Assessment, and Control Options in Food Processing
2018
International Journal of Food Microbiology 2018;285:110-128. Commissioned by the Microbiological Food Safety Task Force.
Risk Assessment or Assessment of Risk? Developing an Evidence-Based Approach for Primary Producers of Leafy Vegetables to Assess and Manage Microbial Risks
2017
Journal of Food Protection: May 2017, Vol. 80, No. 5, pp. 725-733. Commissioned by the Microbiological Food Safety Task Force.
- Salmonella,
- Cronobacter spp. (posing risk to infants),
- pathogenic E. coli,
- B cereus
- Listeria monocytogenes.
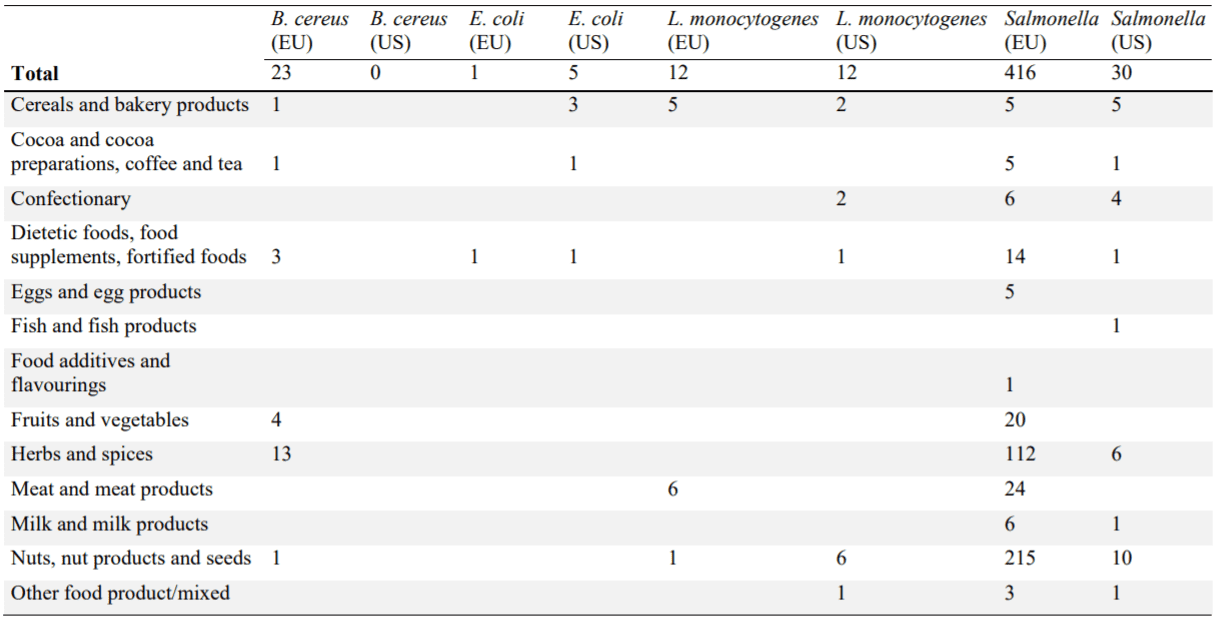
Overview of recalls, withdrawals and safety alerts with microbial pathogens in the EU and US in 2012-2017. EU data were extracted from RASFF (2020) and US data were extracted from FDA (2020).
There is a great interest in the food industry to perform validations in a manner that would be accepted by all parties involved, for example, authorities and customers.
Low moisture foods are foods that:
- are naturally very low in moisture,
- have had water removed from them,
- have a higher moisture content, but that contain agents that prevent the moisture from being available to microorganisms to allow their growth.
In this work, the "production environment" includes production equipment, production surfaces, floors/walls/ceilings, and the air within the production area.
Scientific abstract ExpandProcessing environment monitoring is gaining increasing importance in the context of food safety management plans/HACCP programs, since past outbreaks have shown the relevance of the environment as contamination pathway, therefore requiring to ensure the safety of products. However, there are still many open questions and a lack of clarity on how to set up a meaningful program, which would provide early warnings of potential product contamination. Therefore, the current paper aims to summarize and evaluate existing scientific information on outbreaks, relevant pathogens in low moisture foods, and knowledge on indicators, including their contribution to a "clean" environment capable of limiting the spread of pathogens in dry production environments. This paper also outlines the essential elements of a processing environment monitoring program thereby supporting the design and implementation of better programs focusing on the relevant microorganisms. This guidance document is intended to help industry and regulators focus and set up targeted processing environment monitoring programs depending on their purpose, and therefore provide the essential elements needed to improve food safety.
Keywords Expandcritical control points, pathogen, preventive control, recontamination, Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp., Cronobacter spp., Enterobacteriaceae, dry foods, food safety, processing, environment Monitoring
Low Moisture Foods are defined as having a water activity of 1 or below. In the EU and USA there were 498 combined alerts for microbial pathogens and LMF. Between 2010 and 2017, EFSA reported 10 salmonellosis outbreaks from LMF alone.Genetic characterization of isolates provides interesting insights for understanding the difference between resident and sporadic strains in a processing environment.
[post_title] => Processing Environment Monitoring in Low Moisture Food Production Facilities. Are we looking for the right microorganisms? [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => processing-environment-monitoring-in-low-moisture-food-production-facilities-are-we-looking-for-the-right-microorganisms [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2022-01-26 15:19:39 [post_modified_gmt] => 2022-01-26 15:19:39 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=9564 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => publication [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [1] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 9217 [post_author] => 343 [post_date] => 2021-05-25 07:51:58 [post_date_gmt] => 2021-05-25 07:51:58 [post_content] =>Microbiological Food Safety Task Force
FOOD RELATED CONTAMINANTS
This guidance contains a set of approaches to evaluate available data on target pathogens to support the use of validation studies.
In order to ensure safety of food, a number of control measures need to be implemented by the industry. Validation studies are used to provide evidence that the implemented measures are actually capable of controlling the identified hazard.
Potential to limit the occurrence of discrepancies in the information.
By utilising this guidance, actors involved can identify product and process factors that are essential when designing a validation study. They can thus, select the criteria for identifying an appropriate target pathogen or surrogate organism for a food product and process validation.
Designed for a wide range of food-production professionals.
The document helps food manufacturers, processors, and food safety professionals to better understand, plan, and perform validation studies. It offers an overview of the choices and key technical elements of a validation plan, the necessary preparations including assembling the validation team and establishing prerequisite programs, and the elements of a validation report.
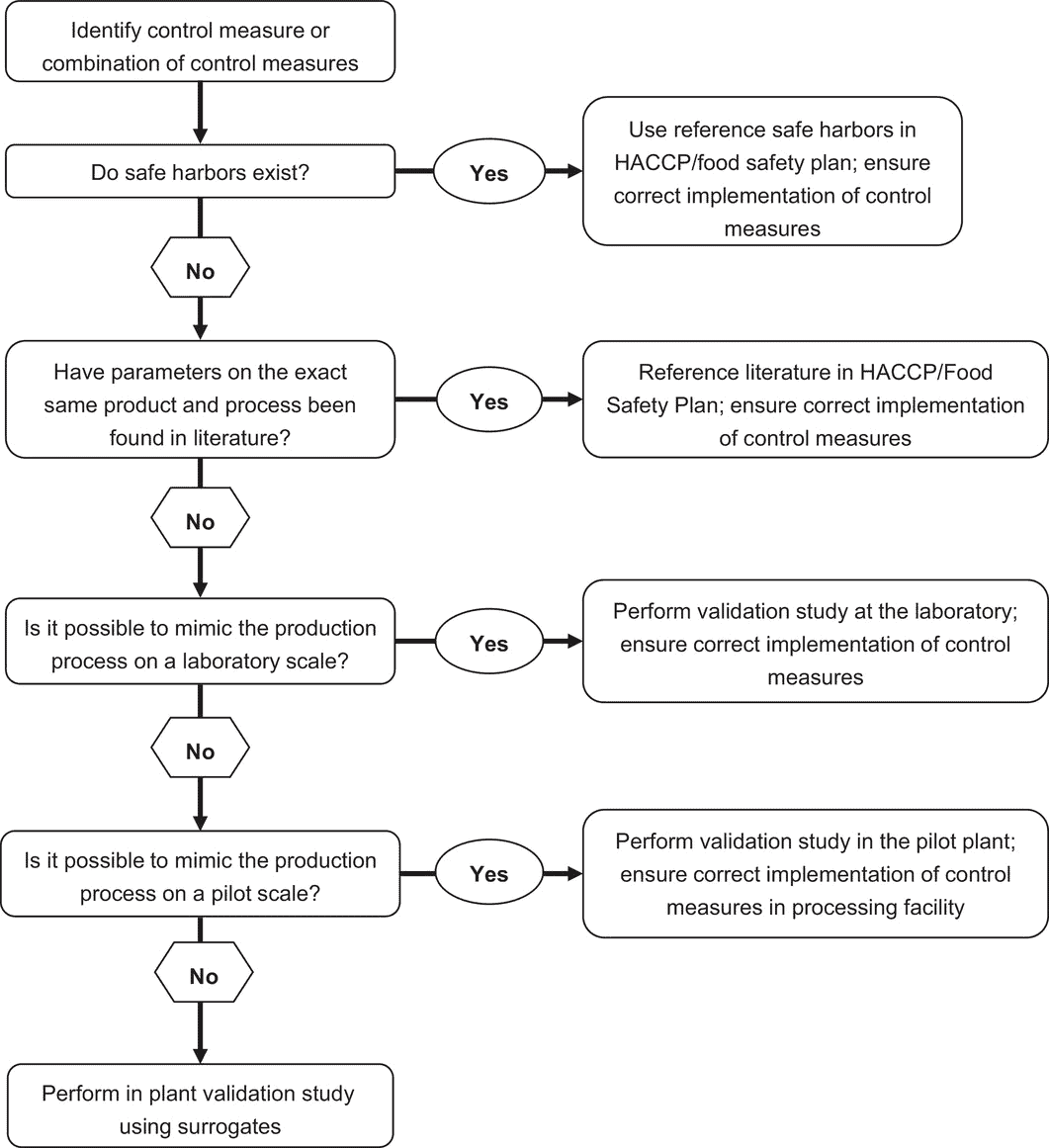
Decision tree to support the decision of when and which validation study approach is most applicable
There is a great interest in the food industry to perform validations in a manner that would be accepted by all parties involved, for example, authorities and customers.
To download this open-access article, please click here.
Scientific abstract ExpandFood manufacturers are required to obtain scientific and technical evidence that a control measure or combination of control measures is capable of reducing a significant hazard to an acceptable level that does not pose a public health risk under normal conditions of distribution and storage. A validation study provides evidence that a control measure is capable of controlling the identified hazard under a worst-case scenario for process and product parameters tested. It also defines the critical parameters that must be controlled, monitored, and verified during processing. This review document is intended as guidance for the food industry to support appropriate validation studies, and aims to limit methodological discrepancies in validation studies that can occur among food safety professionals, consultants, and third-party laboratories. The document describes product and process factors that are essential when designing a validation study, and gives selection criteria for identifying an appropriate target pathogen or surrogate organism for a food product and process validation. Guidance is provided for approaches to evaluate available microbiological data for the target pathogen or surrogate organism in the product type of interest that can serve as part of the weight of evidence to support a validation study. The document intends to help food manufacturers, processors, and food safety professionals to better understand, plan, and perform validation studies by offering an overview of the choices and key technical elements of a validation plan, the necessary preparations including assembling the validation team and establishing prerequisite programs, and the elements of a validation report.
Keywords Expandcritical control points, inactivation, pathogen, preventive control, process validation
Range of nonthermal processing techniques in this study: 10 + the critical parameters for their application and examples. Key factors to consider related to the product 8 They are used to determine process efficiency and whether the target pathogen is capable of growth in product. Food categories for which examples of common pathogens of concern are given 19 + the situations posing increased risk.Validation studies are necessary even when safe harbors are available to ensure correct implementation of control measures.
[post_title] => Guidance on validation of lethal control measures for foodborne pathogens in foods [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => guidance-on-validation-of-lethal-control-measures-for-foodborne-pathogens-in-foods [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2021-07-08 14:16:59 [post_modified_gmt] => 2021-07-08 14:16:59 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=9217 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => publication [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [2] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 6071 [post_author] => 24 [post_date] => 2019-02-11 09:39:27 [post_date_gmt] => 2019-02-11 09:39:27 [post_content] => [post_title] => The Use of Next Generation Sequencing for Improving Food Safety: Translation into Practice [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => the-use-of-next-generation-sequencing-for-improving-food-safety-translation-into-practice [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2019-02-11 09:45:19 [post_modified_gmt] => 2019-02-11 09:45:19 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => http://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=6071 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => publication [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [3] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 5717 [post_author] => 24 [post_date] => 2018-08-08 12:24:25 [post_date_gmt] => 2018-08-08 12:24:25 [post_content] => [post_title] => Foodborne Viruses: Detection, Risk Assessment, and Control Options in Food Processing [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => foodborne-viruses-detection-risk-assessment-and-control-options-in-food-processing [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2021-06-18 12:06:10 [post_modified_gmt] => 2021-06-18 12:06:10 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => http://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=5717 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => publication [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [4] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 4047 [post_author] => 24 [post_date] => 2017-04-20 10:02:04 [post_date_gmt] => 2017-04-20 10:02:04 [post_content] => [post_title] => Risk Assessment or Assessment of Risk? Developing an Evidence-Based Approach for Primary Producers of Leafy Vegetables to Assess and Manage Microbial Risks [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => risk-assessment-or-assessment-of-risk-developing-an-evidence-based-approach-for-primary-producers-of-leafy-vegetables-to-assess-and-manage-microbial-risks [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2020-05-14 12:05:54 [post_modified_gmt] => 2020-05-14 12:05:54 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => http://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=4047 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => publication [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) ) [post_count] => 5 [current_post] => -1 [in_the_loop] => [post] => WP_Post Object ( [ID] => 9564 [post_author] => 343 [post_date] => 2021-08-03 14:26:20 [post_date_gmt] => 2021-08-03 14:26:20 [post_content] =>Microbiological Food Safety Task Force
FOOD RELATED CONTAMINANTS
Prevalence of pathogens of concerns for Low Moisture Foods (LMF) is considered through investigation of the reported foodborne outbreaks.
A Processing Environment Monitory programme (PEM) needs to be in place in order to identify points which need to be routinely sampled, search for harbourage niches, and detect and destroy pathogens of concern. These programmes need to be specifically designed considering the specific pathogens and production set up.
However, a monitoring programme on its own is not sufficient and needs to be accompanied by corrective and preventive action plans to ensure efficient application of the Good Hygiene Practices.
A tool for both food producers and regulators
This guidance document is intended to help set up targeted processing environment monitoring programs depending on their purpose, and therefore provide the essential elements needed to improve food safety.
Several food pathogens are of significant concern when planning monitoring programmes for LMF, and are discussed in this document:
- Salmonella,
- Cronobacter spp. (posing risk to infants),
- pathogenic E. coli,
- B cereus
- Listeria monocytogenes.

Overview of recalls, withdrawals and safety alerts with microbial pathogens in the EU and US in 2012-2017. EU data were extracted from RASFF (2020) and US data were extracted from FDA (2020).
There is a great interest in the food industry to perform validations in a manner that would be accepted by all parties involved, for example, authorities and customers.
Low moisture foods are foods that:
- are naturally very low in moisture,
- have had water removed from them,
- have a higher moisture content, but that contain agents that prevent the moisture from being available to microorganisms to allow their growth.
In this work, the "production environment" includes production equipment, production surfaces, floors/walls/ceilings, and the air within the production area.
Scientific abstract ExpandProcessing environment monitoring is gaining increasing importance in the context of food safety management plans/HACCP programs, since past outbreaks have shown the relevance of the environment as contamination pathway, therefore requiring to ensure the safety of products. However, there are still many open questions and a lack of clarity on how to set up a meaningful program, which would provide early warnings of potential product contamination. Therefore, the current paper aims to summarize and evaluate existing scientific information on outbreaks, relevant pathogens in low moisture foods, and knowledge on indicators, including their contribution to a "clean" environment capable of limiting the spread of pathogens in dry production environments. This paper also outlines the essential elements of a processing environment monitoring program thereby supporting the design and implementation of better programs focusing on the relevant microorganisms. This guidance document is intended to help industry and regulators focus and set up targeted processing environment monitoring programs depending on their purpose, and therefore provide the essential elements needed to improve food safety.
Keywords Expandcritical control points, pathogen, preventive control, recontamination, Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp., Cronobacter spp., Enterobacteriaceae, dry foods, food safety, processing, environment Monitoring
Low Moisture Foods are defined as having a water activity of 1 or below. In the EU and USA there were 498 combined alerts for microbial pathogens and LMF. Between 2010 and 2017, EFSA reported 10 salmonellosis outbreaks from LMF alone.Genetic characterization of isolates provides interesting insights for understanding the difference between resident and sporadic strains in a processing environment.
[post_title] => Processing Environment Monitoring in Low Moisture Food Production Facilities. Are we looking for the right microorganisms? [post_excerpt] => [post_status] => publish [comment_status] => closed [ping_status] => closed [post_password] => [post_name] => processing-environment-monitoring-in-low-moisture-food-production-facilities-are-we-looking-for-the-right-microorganisms [to_ping] => [pinged] => [post_modified] => 2022-01-26 15:19:39 [post_modified_gmt] => 2022-01-26 15:19:39 [post_content_filtered] => [post_parent] => 0 [guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=9564 [menu_order] => 0 [post_type] => publication [post_mime_type] => [comment_count] => 0 [filter] => raw ) [comment_count] => 0 [current_comment] => -1 [found_posts] => 15 [max_num_pages] => 3 [max_num_comment_pages] => 0 [is_single] => [is_preview] => [is_page] => [is_archive] => 1 [is_date] => [is_year] => [is_month] => [is_day] => [is_time] => [is_author] => [is_category] => [is_tag] => [is_tax] => 1 [is_search] => [is_feed] => [is_comment_feed] => [is_trackback] => [is_home] => [is_privacy_policy] => [is_404] => [is_embed] => [is_paged] => [is_admin] => [is_attachment] => [is_singular] => [is_robots] => [is_favicon] => [is_posts_page] => [is_post_type_archive] => [query_vars_hash:WP_Query:private] => 77c00611678cb34f22f035d0e62f7bac [query_vars_changed:WP_Query:private] => [thumbnails_cached] => [allow_query_attachment_by_filename:protected] => [stopwords:WP_Query:private] => [compat_fields:WP_Query:private] => Array ( [0] => query_vars_hash [1] => query_vars_changed ) [compat_methods:WP_Query:private] => Array ( [0] => init_query_flags [1] => parse_tax_query ) )Multimedia
- Microbiological Food Safety Task Force – One-pager
- The Microbiological Food Safety Task Force in a nutshell, an introductory video*
* The video was developed on the occasion of the Annual Symposium
‘Practical guidance for validation studies: from start to finish’
Watch the Webinar
‘Foodborne Viruses: Detection, Risk Assessment, and Control Options in Food Processing’
Watch the Webinar
